Wide Awake: Autism, Insomnia and Me
by musingsofanaspie, musingsofanaspie.comNovember 29th 2012
Like a lot of what I experience because of Asperger’s, until I started reading about insomnia, I didn’t realize that I’ve suffered from it on and off since I was a child.
Apparently, I’ve always had slightly abnormal sleeping habits. Sometimes it takes me a long time to fall asleep. Some nights I wake up a half dozen times; others (like today) I wake up at 3:00 AM feeling like it’s the middle of the afternoon. I can hit the ground running at 5:00 AM with an energy level that seems to piss people off.
In more technical terms, I have classic signs of autism-related insomnia:
- prolonged sleep latency (time to fall asleep)
- reduced sleep efficiency (decreased time asleep/time in bed)
- reduced total sleep time
- reduced sleep duration and continuity
- night awakening exemplified by of long periods of time awake1
I was shocked to learn that the prevalence of insomnia in children with ASD is 40% to 80%.2 When you read about typical symptoms of autism and Asperger’s, sleep disturbance is not only missing from the core list of diagnostic symptoms, it’s rarely mentioned at all.

A Budding Insomniac
My parents adopted a benign disinterest when it came to my sleep habits. They put me in bed at eight o’clock and the rest was up to me. I’d make multiple trips to the bathroom for a drink of water or to take one last pee (three or four or more times) but as long I didn’t bother my parents, they didn’t make a fuss about whether I was actually sleeping.
I had a nightlight beside my bed and most nights I’d hang over the side of the bed, reading until I felt tired. Before I was old enough to read, I would sit at the top of the steps and listen to what was going on downstairs to pass the time until I felt tired. In my teens I got a portable black and white TV for my birthday and I’d watch TV, using earphones so I wouldn’t get caught.
I think my parents knew about these habits–they occasionally pointed out that I’d go blind if I kept up my “reading in the dark” and more than once they shooed me back to bed from the bottom of the steps. On an average night, though, my parents’ bedside lights had been turned off by the time I made my last couple of trips to the bathroom.
When I woke in the night, which happened most nights, I’d call my dad and he would lie down in my bed while I went to the bathroom. I’m not sure what purpose this served except that I remember being a little afraid of the dark after walking into a wall and getting a bloody nose one night. I guess it was reassuring to know that if I did it again, at least my dad would be there to hand me some tissues.
My parents’ laissez-faire attitude toward my sleep problems taught me two things: (1) it’s not a big deal and (2) you’re responsible for putting yourself to sleep. The second part sounds a bit harsh, but because they never made an issue out of when or how much I was actually sleeping, it never felt that way. A little lonely perhaps, but I also liked those few hours at night when everyone else was asleep and the house was quiet. I got to indulge in my special interest (reading) and that was calming, which eventually lulled me to sleep.
Granted, if I’d been destructive or intent on going out to roam the neighborhood, this strategy wouldn’t have worked.
What Works for Me
As an adult I’ve learned that having the right sleep conditions makes a big difference for me. Some things that help me sleep better:
1. Plenty of exercise during the day. I need to be physically tired to sleep well so getting in at least an hour of walking, running and/or swimming every day is essential.
2. Heavy blankets. The slight pressure of a heavy comforter and blankets relaxes me. If I only have a sheet or light blanket, I’ll wake up repeatedly.
3. A cool room. I tend to overheat when I sleep. I’m not sure if this is Aspergers-related, but if the room is even slightly warm, I’ll wake up sweating.
4. Comfortable clothes. As a kid I wore snug fitting pajamas. I still can’t sleep in anything that’s too loose, like a nightgown, because I end up feeling like it’s strangling me the first time I turn over.
5. Familiar surroundings. It’s much easier to relax when I’m in a familiar environment. If I go on vacation or move to a new place, it takes me a few days to “learn” to sleep there because my brain needs to catalog the unfamiliar sounds and smells.
6. A quiet environment or consistent noise. I need either total quiet or a consistent natural noise (wind, waves, steady traffic) to fall asleep. Something like intermittent voices, a radio or a television–even one playing in the apartment above or below me or in an adjoining hotel room–will keep me awake until it stops. In fact, I’ll usually be awake long after it stops because of the anxiety it generates.
7. A dark room. I can’t sleep unless the room is completely dark. Light shining in my room through a window or under/around a door will keep me up. The flashing light of a muted television drives me nuts.
8. Reading (or enjoying a special interest) before bed. Reading has been one of my special interests since childhood. Like any special interest, it distracts and calms me. I think it’s also become a sleep cue. When I pick up a book in bed, my brain starts sending out sleep signals to my body. It usually only takes 15-20 minutes of reading before I start to feel myself drifting off.
9. A light dinner and no snacks after dinner. I fall asleep faster and sleep better if I have a low-fat, low-sugar dinner and give myself at least a few hours to digest it before going to bed
Those are the things that I’ve discovered over the years work for me. I’d love to hear from others on the spectrum who’ve discovered tricks for getting to sleep or staying asleep.
Recently I was talking with my daughter about my sleep habits and she asked why I don’t try to resolve my insomnia. I told her that it doesn’t bother me–I use my middle-of-the-night time to read or think–or impact my daily life. Her response was, “Maybe it does impact you and you don’t realize it because you’re so used to it.” There’s a lot of wisdom in that statement. Something to think about, for sure.
(Unless you’re a geek like me, you can safely stop reading here.)
A Little Geekery About Melatonin and Circadian Rhythm to Wrap this Up
There are a few theories about why so many people with ASD have sleep problems. One of the most prevalent theories points to abnormal melatonin levels.2 Consequently, many children with ASD-related insomnia are given melatonin to induce more regular sleep habits. From what I’ve read anecdotally, this works well for many children and results in unacceptable side effects for some.
Another, lesser-known theory that caught my attention suggests that neurodevelopmental disorders increase the likelihood of sleep disturbances due to an inability to perceive and interpret sleep-related environmental cues.3 This is obviously far more difficult to measure and quantify in a lab than melatonin levels (which are easily measured in blood plasma). But it got me digging for more details because so much of my Asperger’s seems to trace back to the dysfunctional processing and filtering of my environment.
Caution: amateur scientist at play: I learned that our circadian rhythm (the internal clock responsible for, among other things, when we sleep) relies on external inputs to regulate sleep. The natural light-darkness cycle is the primary input, but our circadian rhythm can also be affected by our rest/activity schedule, mealtimes and social interaction. All of these inputs pass through a “central pacemaker” in the brain, which “outputs” various hormones that act as signals to the rest of the body and regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
Here’s a nifty graphic showing the “input” and “outputs” of the human circadian system4:
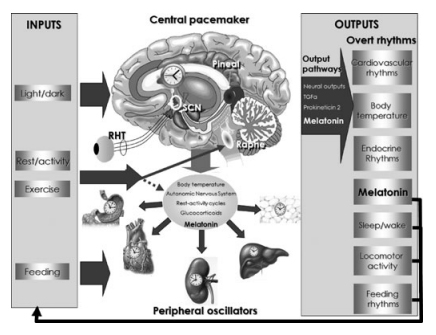
The really interesting part is that the body can’t maintain an accurate 24-hour circadian rhythm without the input of environmental cues. Our natural circadian rhythm, in the absence of environmental cues, is 25-27 hours. Whoa!
Perhaps dysfunctional processing of one or more circadian inputs throws off the circadian rhythm, leading to the abnormal levels of melatonin (a key output) found in many people with ASD.
The dysfunctional processing theory would explain why many of the things I do to help me sleep better qualify as circadian inputs: exercise, consistent activity cues around bedtime, no eating close to bedtime, and a dark room. Over the years I’ve developed inputs that tell my body loud and clear: calm down and go to sleep.
It doesn’t always work but I have a feeling things could be a lot worse.
References:
1Goldman, Suzanne et al. “Parental Sleep Concerns in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Variations from Childhood to Adolescence” J. Autism Dev Disord, 2012, (42) 531-538.
2Souders MC; Mason TBA; Valladares O; Bucan M; Levy SE; Mandell DS; Weaver TE; Pinto-Martin D. Sleep behaviors and sleep quality in children with autism spectrum disorders. SLEEP 2009;32(12):1566-1578.
3Williams, P. Gail et al. “Sleep problems in children with autism” J. Sleep Res. (2004) 13, 265–268.
4Escames, G., Ozturk, G., Baño-Otálora, B., Pozo, M. J., Madrid, J. A., Reiter, R. J., Serrano, E., Concepción, M. and Acuña-Castroviejo, D. (2012), Exercise and melatonin in humans: reciprocal benefits. Journal of Pineal Research, 52: 1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00924.x
Original Page: http://pocket.co/sh_JG
Shared from Pocket
No comments:
Post a Comment